Gen AI: What are the key concepts and technologies?
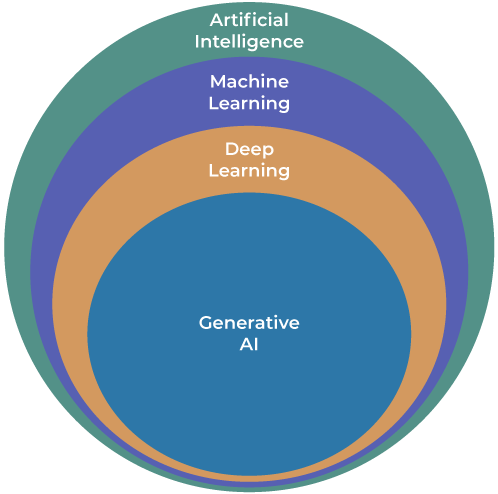
AI is not just one technology. Rather, it is an entire field of study in the same way that something like physics is.
Similarly, while physics has numerous branches or subfields – such as thermodynamics, electromagnetism, and quantum mechanics – so too does AI:
- Machine learning (ML), for instance, is a subfield that lies at the core of AI.
- Dig down a bit further and you’ll discover deep learning (DL), which is a subfield of ML.
- DL, in turn, serves as the foundation on which many generative AI models are built.
In essence, each concept or technology builds upon the previous one.
***
Get weekly insights from The Intuition Finance Digest. Elevate your understanding of the finance world with expertly-crafted articles and podcasts sent straight to your inbox every week. Click here: https://www.intuition.com/finance-insights-the-intuition-finance-digest/
***
Machine Learning
We can view AI as setting the overall goal of creating systems that mimic human intelligence.
ML, meanwhile, provides the means to achieve AI through data-driven learning. Using algorithms and statistical models, it enables computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without the need for explicit instructions or programming.
There are a number of different types of ML:
- Supervised ML
- Unsupervised ML
- Semi-supervised ML
- Reinforcement Learning (RL)
Deep learning & neural nets
Traditional supervised and unsupervised machine learning techniques use basic mathematical and statistical tools to process data and produce outputs.
But their capabilities are relatively modest compared to human intelligence.
For many computer scientists, these techniques cannot produce “true” AI – or more specifically, artificial general intelligence systems.
AGI, or strong AI, possesses the full spectrum of human abilities, including understanding speech and natural language, decision-making, and all other daily tasks and competencies that require intelligence.
To achieve this, AGI would theoretically have to be modeled on the human brain, simply because this is the only model we know that can produce human intelligence.
An AGI would, therefore, use digital analogs of the complex neurological and biological processes that underlie human cognitive processes.
So, to develop more advanced forms of AI, computer scientists and programmers created artificial neural networks intended to mimic the human brain.
These neural nets are the backbone of deep learning, or DL for short.
This subset of ML uses artificial neural networks to recognize patterns and make decisions based on large amounts of data.
Deep learning is modeled on the structure and function of the human brain, with multiple layers – hence the word “deep” – of interconnected nodes that process data in parallel.
DL algorithms thus analyze data with a logical structure similar to how humans draw conclusions.
Depending mostly on the type of problem it is being used to solve and the available data, deep learning may be supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, or reinforcement-based.
It has pushed the boundaries of what AI can achieve in terms of creativity and data generation, and deep learning algorithms are at the core of many GenAI models today.

GenAI & transformer models
As you know if you’ve used any GenAI tools, this is a technology that enables users to create (generate) new content by inputting prompts.
GenAI operates through various different models that learn the patterns and structure of their input training data and then generate new data (outputs) with similar characteristics.
Input and output data can include text, images, audio/sound, video/animation, code, and more. It generates new content from and into any of these (and other) modalities – for example, text-to-image and video-to-text.
As mentioned above, GenAI tools are based on different models. ChatGPT, for instance, is a “transformer” model. A transformer is a deep learning architecture developed by Google and made public in 2017. Since then, it has been the basis for much of the exponential progress in natural language processing (NLP) and, more broadly, GenAI. These models excel at analyzing sequential data, such as text, by establishing relationships between words within the sequence and then transforming it into an output sequence.
Many contemporary GenAI tools are based on this transformer architecture – apart from ChatGPT, other well-known examples include Claude, Gemini, and Cohere.
The content for this article is taken directly from Intuition Know-How, our flagship digital library that gives finance professionals fast, flexible access to high-impact content, including a full learning channel dedicated to AI and FinTech.
Fill in the form below to view all Intuition Know-How content.
Browse full tutorial offering



