Blockchain Bonds Could Slash Costs
But Serious Investment Is Needed to Modernize the Industry
Like trade finance, bond markets have traditionally been manual, paper-intensive, and tech-shy. Outside of large, liquid markets like US Treasuries, fixed income trading is often done over the counter (OTC) and bond issuance involves large volumes of paperwork and manual documentation. New technologies such as blockchain have the potential to revolutionize these old-fashioned processes and several proof-of-concept blockchain bond issues have shown the cost-cutting and efficiency-boosting potential of new tools. The true test, however, will be whether market participants are willing to make the investments necessary to transform the bond market.
In April 2021, the European Investment Bank (EIB) launched a digital bond issue on a blockchain platform. The EIB, in collaboration with Goldman Sachs, Santander, and Société Générale, used a distributed ledger to register and settle a €100 million, two-year bond issue.
Interestingly, the EIB partnered with Banque de France to have the payment of the issue monies from the underwriters represented on the blockchain in the form of a central bank digital currency (CBDC). The banks that syndicated the bond paid for digital bond tokens that were registered on the public Ethereum blockchain network. The EIB then used Banque de France’s CBDC to settle the bond with the arrangers.
The EIB transaction was just the latest in a string of blockchain bond and debt instrument issues. Also in April, for example, Société Générale issued a structured product using blockchain, and Vonovia, UnionBank, Standard Chartered, and many others have all been involved in digital bond issues.
In all the above examples, the securities in question – bonds, notes, or structured products – were issued not in the form of physical certificates, but rather as digital records on a publicly permissioned blockchain ledger.

Blockchain benefits
Widespread interest in blockchain bond issuance is being driven by the desire to improve efficiencies and lower costs in the traditionally bureaucratic and decentralized bond market.
In traditional bond issuance – and, indeed, securities issuance more broadly – the process is manual and paper-intensive. Multiple players are involved, and there is significant record-keeping redundancy across the network of participants, which necessitates expensive and time-consuming reconciliation between their different systems. The diffused process also leads to a long clearing and settlement cycle – generally T+3 – creating high levels of settlement risk. The number of intermediaries also creates high costs as issuers and investors incur fees at multiple points in the process.
Overview of Securities Issuance Process:
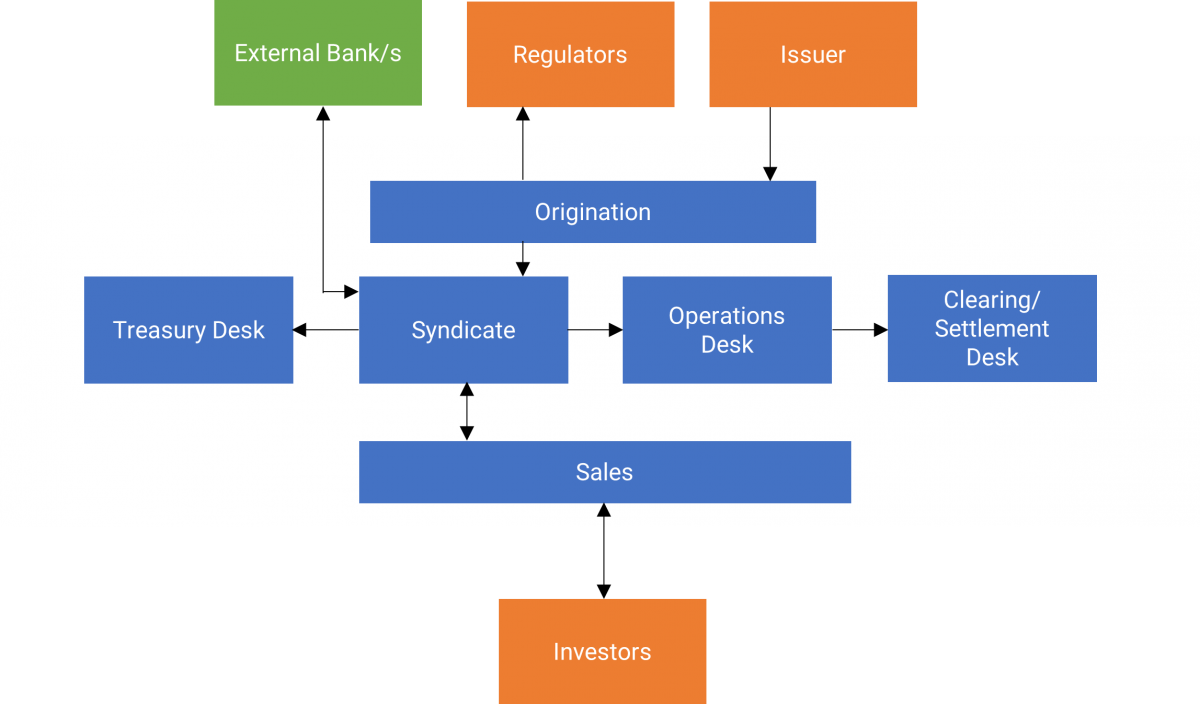
Source: Capgemini. Blockchain Disruption in Security Issuance. 2017.
The use of a decentralized and secure ledger or database – a blockchain – dramatically reduces the number of intermediaries involved in bond issuance, as well as reducing ongoing custody and asset servicing costs. Blockchain enables near real-time bookbuilding and removes the need for reconciliation as all participants have access to the same immutable transaction ledger. Settlement risk is slashed thanks to rapid clearing and settlement and the reduction in intermediaries eliminates many fees.
A 2020 study by German FinTech firm Cashlink and custody provider Finoa found that using tokenization (issuance in the form of digital tokens using a blockchain platform) rather than traditional securitization could achieve costs savings of 35 to 65%. While pre-issuance costs, such as the legal fees involved in structuring an issue, were comparable for both tokenization and securitization, all other costs were substantially lower for tokenization, including custody services, trading costs, and so on. Furthermore, the strong cryptography associated with blockchain adds a layer of data protection and cybersecurity to the issuance process.
Some observers are particularly excited about the potential of blockchain bond issuance to revolutionize capital markets in emerging economies. By reducing costs and slashing the number of intermediaries involved, blockchain issuance could open up the bond market to small and medium enterprises in emerging markets, which have traditionally struggled to secure the funding they need.

Roadblocks
While blockchain technology offers many advantages, uptake in bond markets has been relatively slow. Most issues to date have been prototypes or proofs-of-concept and few have resulted in the creation of long-term issuance platforms.
One key roadblock is regulation. The EIB issue described above was done in France because French law allows for the registration of digital securities to be recognized as financial securities. Few other jurisdictions allow this, limiting opportunities for tokenization – this is especially true in emerging markets, where regulators have generally been slower to implement technology-enabling rules.
Another is investment. Financial market players will need to invest significantly in new platforms and tools to make blockchain issuance the norm rather than the exception. Protocols and standards must be developed, and institutions must agree on a range of technical and procedural details.
Blockchain has the potential to transform bond issuance. By lowering costs, it could democratize access to finance and create more efficient capital markets. However, until governments create enabling regulatory environments and market participants make the necessary investments, blockchain bond issuance risks being a novelty rather than a mainstream capital-raising option.
Intuition Know-How has a number of tutorials that are relevant to bonds and blockchain policies:
- Bond Markets – An Introduction
- Bond Markets – Issuing
- Bond Markets – Trading
- Cryptography
- Blockchain – Primer
- Crypto Assets
- US Bond Market
- UK Bond Market
- European Bond Market
- Japanese Bond Market


